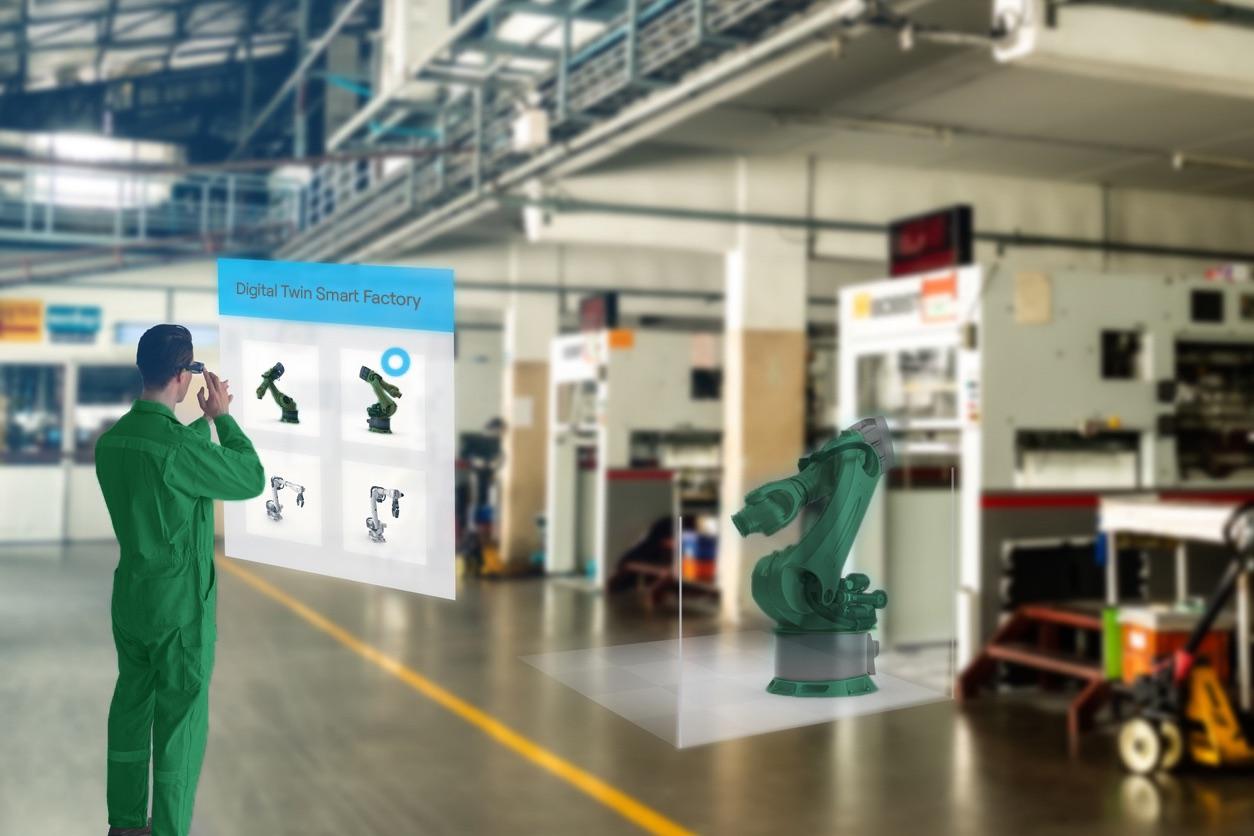
The Digital Twin is a tool that allows to simulate production scenarios on a process or a physical asset and to represent the results on the digitisation of the components.

Índice del contenido
Digital Twin: What is it?
Digital Twins: Features
Digital twins allow factory managers to make strategic decisions about the operation of their processes and management of their assets based on the analysis of different simulated scenarios, without jeopardising production or the integrity of plant equipment.
.
The digital twin consists of 3 fundamental levels for a successful implementation:
- Sensorisation of the processes or assets subject to be implemented within the Digital Twin to obtain the correct inputs (Data) that will be used to feed the analytical model. It is possible that these data are already available in factory control systems and only need to be unified.
- Analysis of the data obtained and design of the simulation models necessary to obtain the desired outputs.
- Visualisation of the information obtained in the simulation to make decisions quickly and accurately.
Types of digital twins
After knowing what digital cufflinks are and their characteristics we proceed to discover the different types of digital twins.
- Digital product Twin
The digital product twin is based on simulating the existence of a product in different conditions. In this way, the adaptability of the product to different situations and obstacles will be observed in order to make the necessary adjustments and thus guarantee the correct functioning of the next product.
- Digital production twin
The digital production twin is based on simulating the interaction of different production processes to verify production efficiency. That is to say, through the analysis of all the simulated processes it will be possible to know which ones must be modified so that errors do not occur and which ones are working correctly.
- Digital Performance Twin
Production plants and products that are part of Industry 4.0 constantly generate data. This data can be collected by the digital performance twin for analysis and informed decision making.
Digital Twins Applications
The applications of the digital twin can be various, depending on the needs of each factory, although the most common are the simulation of production lines based on different operating parameters or the predictive maintenance of physical assets.
- Digital Twin applications in production processes
Applying the digital twin to production lines allows us to know what effects certain operational changes or modification of rates such as breakdowns or stoppages may have on the KPIs of the process in question.
- Digital Twin applications for logistics flow simulations
Digital twins can also be applied to logistics processes to optimise intralogistics routes for forklifts or AGVs and make changes in the simulation to help us make decisions about restructuring the process or incorporating new elements.
- Digital Twin applications in physical assets
In this case, the digital twin can be applied to the simulation of machine behaviour depending on different operating parameters without compromising its integrity, this usually makes sense in the most critical plant assets.