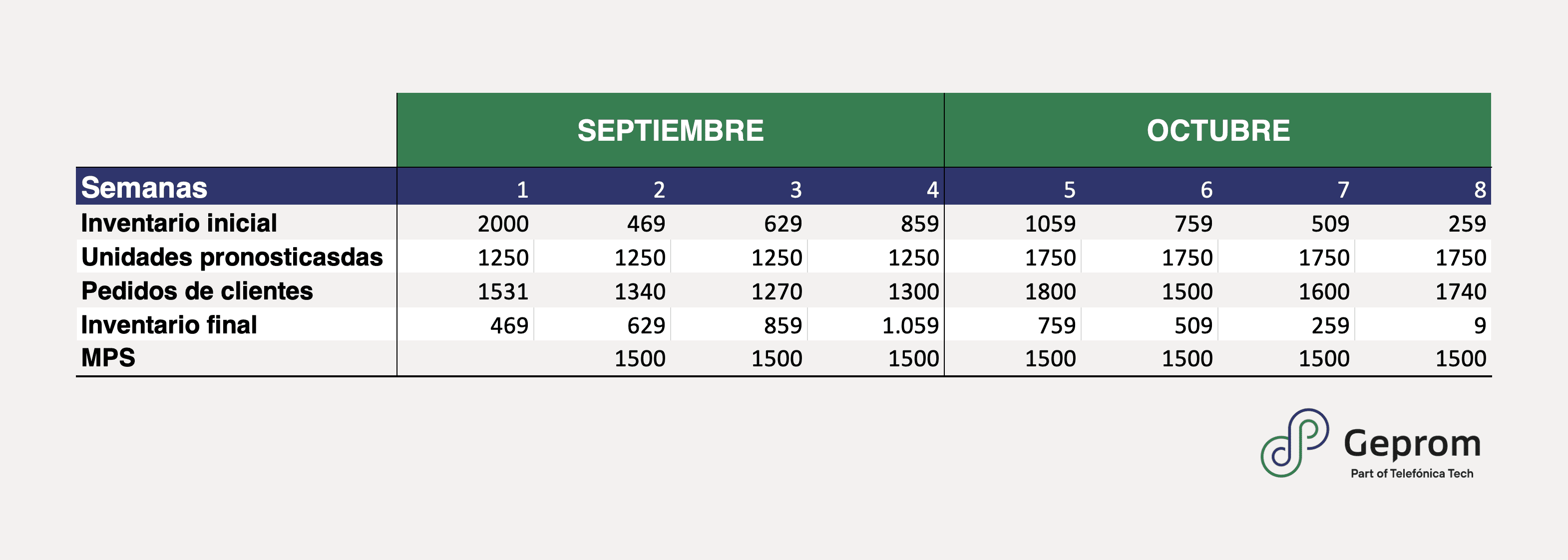
A Master Production Plan (MPS or PMP) is the document that contains a detailed manufacturing plan of the references to be produced in our factories in a given period of time. It is an extremely important element in the operations department of any productive company and needs to be nurtured by different areas in order to be executed successfully.
With the PMP we can determine, through the different production or manufacturing orders (PO or OF), the specific volumes of each product that we are going to manufacture in the short term, generally, with a weekly or biweekly vision and always having as a minimum point the manufacturing cycle of the product itself. The PMP must consider the final product, available for shipment to the end customer, and reflect in detail the planning of by-products or intermediate products.